>
Spotlight April 2023: Recycling rare earths – bacteria assist in the circular economy
>
Spotlight April 2023: Recycling rare earths – bacteria assist in the circular economy
Rare earths are important components of wind turbines, catalytic converters, fibre optic cables and plasma screens. Since the 17 metals grouped under this term are indispensable for modern technologies, demand and costs are constantly rising. The occurrence of productive mining sites is limited and the production is often costly and environmentally harmful. The advantages of recycling these resources as efficiently as possible, for example from industrial waste water in the fields of mining, electronics or chemical catalysts, are obvious.
In cooperation with the University of Kaiserslautern, researchers at the Technical University of Munich have taken the circular economy of these demanded metals a huge step further: they examined several strains of cyanobacteria for their potential to bind rare earths from aqueous solution – and were successful.
The researchers determined the potential for the so-called biosorption of the rare earths lanthanum, cerium, neodymium and terbium for twelve strains of cyanobacteria. Most of these strains had never before been investigated for biotechnological potential. They come from habitats with extreme environmental conditions.
In a further project, the scientists plan to carry out the experiments on a larger scale in order to advance the industrial application of the results.
Original publication:
Michael Paper, Max Koch, Patrick Jung, Michael Lakatos, Tom Nilges and Thomas B. Brück: Rare Earths Stick to Rare Cyanobacteria: Future Potential for Bioremediation and Recovery of Rare Earth Elements. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol., Sec. Bioprocess Engineering, Volume 11 – 2023

Weitere Spotlights
Spotlight August 2020: The nanoGRAVUR Grouping approach
In August, we would like to present a paper of the German BMBF project nanoGRAVUR. nanoGRAVUR dealt from 2015-2018 with the grouping of nanostructured materials with regard to occupational safety, consumer and environmental protection and risk mitigation. The approach is now described by the project partners in this paper.Due to the variety of synthetic nanomaterials and the numerous modifications (differences in size, shape, chemical composition and surface functionalization), the effort required to investigate effects and behaviour within the framework of regulatory requirements is…
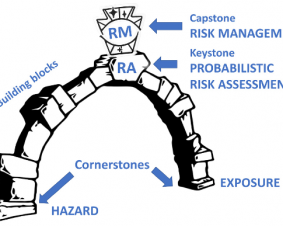
Read moreSpotlight February 2022: Probabilistic risk assessment – the keystone for the future of toxicology
The basics of toxicology are constantly being reconsidered, and the approach to risk assessment is therefore constantly being put to the test, because, as William Osler is cited in this publication, “Medicine (toxicology) is a science of uncertainty and an art of probability“. In this recent paper, the team around Thomas Hartung (Johns-Hopkins University/University of […]
Read moreSpotlight July 2021: The Path to Digital Material Research – It is never too late to start
Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence, Big Data…. Have you read these words lately? No, these are not just buzzwords. The digitalisation of science is an evolving topic that is gaining importance with each passing day. That is why this month we would like to introduce you to the article “Digital Transformation in Materials Science: A Paradigm […]
Read moreSpotlight June 2021: Endotoxin – the reason for false-positive toxicity testing for advanced materials?
Advanced materials, but also nanomaterials are closely examined to determine whether they trigger biological effects that could be harmful to humans and the environment before they are used in products. This also includes such materials as titanium dioxide, which has been used in a wide variety of products for more than 50 years. A particularly […]
Read more