>
Spotlight December 2022: Fighting tumors with micro robots
>
Spotlight December 2022: Fighting tumors with micro robots
When we, the DaNa team as operators of the website nanopartikel.info, write about nanobots, i.e. nanometre-sized machines, we point out that these machines belong to science fiction, may even remain a utopia – i.e. never realisable. On the significantly larger micro-scale, however, small machines are conceivable that could help in the therapy of diseases, e.g. cancer. Such an approach is now presented by S. Schürle from ETH Zurich, who is developing magnetically controllable microrobots. She is using naturally occurring bacteria that have a magnetic “core” and with the help of which they can be steered to the target as microrobots.
This approach is not entirely new in terms of the basic idea, but it is significantly improved by the Zurich working group because rotating magnetic fields are used to make the bacteria rotate. The impression is that the microrobots now work like micro-drilling machines and drill their way non-destructively between cells to get from blood vessels through the blood vessel wall to tumour cells. You can read about the results she has achieved and the new approaches S. Schürle is exploring on the ETH Zurich website and in the original publication cited there (Gwisai T, Mirkhani N, Christiansen MG, Nguyen TT, Ling V, Schuerle S: Magnetic torque-driven living microrobots for increased tumour infiltration, Science Robotics 26 October 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/scirobotics.abo0665)
Weitere Spotlights
Spotlight April 2021: Nanomaterials and Fake News – a commentary based on an example
In February 2021, the article “The invisible killer lurking in our consumer products” appeared, describing nanoparticles as a greater danger than Corona [1]. “The use of nanomaterials” would be “unregulated” and “nanomaterials are so small that they cannot be determined once they are part of a product”. So what is the truth of these statements? […]
Read moreSpotlight September 2021: Wood, the raw material of the future?
One of the greatest challenges facing humanity is to produce clean drinking water under the given circumstances of global warming, population growth and increasing littering. In September, we would like to present a review article that believes one approach to solve this problem is the use of nanoscale wood. In the review, “Advanced Nanowood Materials […]
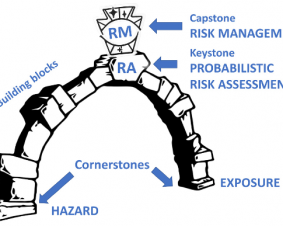
Read moreSpotlight February 2022: Probabilistic risk assessment – the keystone for the future of toxicology
The basics of toxicology are constantly being reconsidered, and the approach to risk assessment is therefore constantly being put to the test, because, as William Osler is cited in this publication, “Medicine (toxicology) is a science of uncertainty and an art of probability“. In this recent paper, the team around Thomas Hartung (Johns-Hopkins University/University of […]
Read moreSpotlight March 2023: How can photovoltaics be made safe and sustainable?
Conventional photovoltaic systems often have only low efficiency, i.e. only a fraction of the solar energy is converted into electrical energy and made usable. For this reason, research is being conducted into innovative materials that can significantly increase the energy yield and thus also enable more electrical energy to be generated from renewable sources. However, […]
Read more