>
Spotlight January 2021: Nanoplastics challenge – How to improve tracking of nanopolystyrene distribution in the environment.
>
Spotlight January 2021: Nanoplastics challenge – How to improve tracking of nanopolystyrene distribution in the environment.
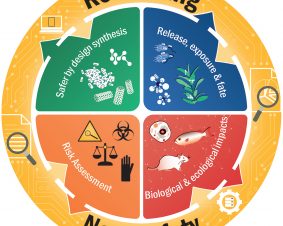
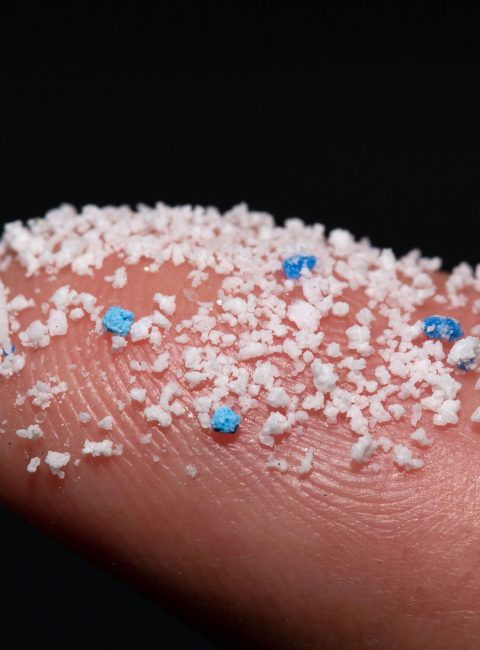
In January, we present a paper published in the Nature Journal communications materials. The article focuses on the development of a new detection method of nanopolystyrene. The method not only makes it possible to detect nanoplastics in the environment for the first time, but also to determine their accumulation in plants and animals.
Nanoplastics, which are added to numerous commercial products or are created by further breaking down microplastics, pose a major threat to our environment. Detection in the environment is difficult for two reasons. First, the small size makes it difficult to detect the particles in the environment. Second, the concentrations are very low. However, tracking nanoparticles is essential to understand potential effects on plants and animals. The team led by Maya Al-Sid-Cheikh has succeeded in improving the detection of nanoplastics by using a special label. To do this, they used a special form of carbon, called 14C, which does not occur naturally. Unlike other labels, e.g. fluorescent dyes, this label cannot be lost, e.g. by fading. By using such 14C-labeled polystyrene particles, the uptake and distribution of nanoplastics in mussels could be tracked for the first time. The 14C-labeled nanopolystyrene could be detected even in very low concentrations, which also allows detection in the environment, e.g. lakes or rivers. The method can be used to better understand the distribution of nanoplastics in the environment and in organisms by means of laboratory experiments. However, it does not allow direct measurement of nanoplastics in the environment because they do not carry the label. As the authors also critically note, it is possible that labeled particles and naturally occurring particles behave differently.
Original publication:
Al-Sid-Cheikh, M., Rowland, S.J., Kaegi, R. et al. Synthesis of 14C-labelled polystyrene nanoplastics for environmental studies. Commun Mater 1, 97 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43246-020-00097-9

Weitere Spotlights
Spotlight April 2021: Nanomaterials and Fake News – a commentary based on an example
In February 2021, the article “The invisible killer lurking in our consumer products” appeared, describing nanoparticles as a greater danger than Corona [1]. “The use of nanomaterials” would be “unregulated” and “nanomaterials are so small that they cannot be determined once they are part of a product”. So what is the truth of these statements? […]
Read moreSpotlight Juli 2020: “Nanosafety – More than just regulatory processes”
Nanosafety is more than just a compulsory aspect of nanomaterials research and regulation. This research area also has great potential to drive new innovations. It is exactly this perspective that is addressed in the special issue “Rethinking Nanosafety: Harnessing Progress and Driving Innovation” by Chen et al. 2020. The article illustrates that especially in the field of […]
Read moreSpotlight March 2021: Is Nanotechnology the Swiss Army Knife against Future Pandemics?
The COVID 19 outbreak has led to a fundamental rethinking of existing approaches to diagnosis, treatment, and prevention methods. The need for better and more efficient concepts is global and urgent. Nanotechnology has long been at the forefront of innovation and has led to advances in many different disciplines. Could this interdisciplinary field help develop […]
Read moreSpotlight September 2021: Wood, the raw material of the future?
One of the greatest challenges facing humanity is to produce clean drinking water under the given circumstances of global warming, population growth and increasing littering. In September, we would like to present a review article that believes one approach to solve this problem is the use of nanoscale wood. In the review, “Advanced Nanowood Materials […]
Read more