>
Spotlight February 2022: Probabilistic risk assessment – the keystone for the future of toxicology
>
Spotlight February 2022: Probabilistic risk assessment – the keystone for the future of toxicology
The basics of toxicology are constantly being reconsidered, and the approach to risk assessment is therefore constantly being put to the test, because, as William Osler is cited in this publication, “Medicine (toxicology) is a science of uncertainty and an art of probability“.
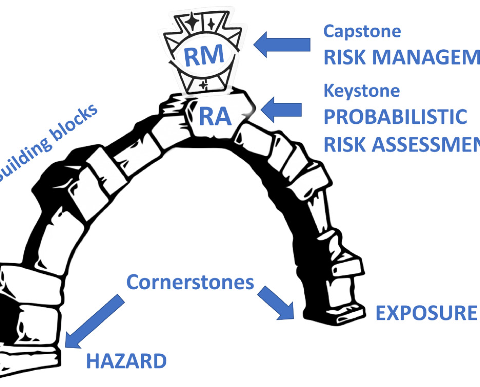
In this recent paper, the team around Thomas Hartung (Johns-Hopkins University/University of Konstanz) has shown that for improved toxicology we should rather work with a “Probabilistic Risk Assessment” approach. This is also or especially important for new materials, because with these there are particularly often gaps in knowledge, uncertainties in risk assessment due to conflicting data and the most diverse hypotheses and strategies of the various stakeholders. In the publication, various models are presented that are applicable for this type of risk assessment and for some of which corresponding software is also available to perform calculations for the respective exposure scenarios. In the examples for this approach, a paper by Jacobs et al. (1) is also cited here, who had applied the case to silica in food. They concluded that after taking all uncertainties into account and using all available data, the margin of safety has not yet been exceeded by far using silica in various food products. In 2017, an international group of experts applied this method to Titanium dioxide in seven different exposure scenarios and concluded no increased risk to humans, as the probability of exceeding the safety limits is vanishingly small (2).
The suggested approach by Johns Hopkins University is thus a good indication to adopt this method in order to be able to make a reasonable risk assessment for new, innovative materials even in the presence of uncertaintie.
Further literature:
- Jacobs, R., van der Voet, H., and Ter Braak, C.J. (2015). Integrated probabilistic risk assessment for nanoparticles: the case of nanosilica in food. J Nanopart Res 17, 251
- Tsang, M.P., Hristozov, D., Zabeo, A., Koivisto, A.J., Jensen, A.C.O., Jensen, K.A., Pang, C., Marcomini, A., and Sonnemann, G. (2017). Probabilistic risk assessment of emerging materials: case study of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 11, 558-568
Original publication:
Maertens, A., Golden, E., Luechtefeld, T.H., Hoffmann, S., Tsaioun, K., and Hartung, T. (2022). Probabilistic risk assessment – the keystone for the future of toxicology. ALTEX 39, 3-29
Weitere Spotlights
Spotlight January 2022: Methods, models, mechanisms and metadata
For the new year, we are presenting no “classic” paper here, but would like to point out an editorial: Methods, Models, Mechanisms and Metadata: Introduction to the Nanotoxicology Collection at F1000 Research. This editorial introduces the F1000Research Nanotoxicology Collection, where best practices can be collected in the form of original research reports, including no-effect studies, […]
Read moreSpotlight December 2022: Fighting tumors with micro robots
When we, the DaNa team as operators of the website nanopartikel.info, write about nanobots, i.e. nanometre-sized machines, we point out that these machines belong to science fiction, may even remain a utopia – i.e. never realisable. On the significantly larger micro-scale, however, small machines are conceivable that could help in the therapy of diseases, e.g. […]
Read moreSpotlight September: A methodology for the automatic evaluation of data quality and completeness of nanomaterials for risk assessment purposes
This paper describes a method for automatically assessing the quality and completeness of nanosafety data for the purpose of risk assessment. Steps to develop the methodology for assessing data completeness and the methodology for assessing quality are presented. The methodology is tailored to physicochemical and hazard (meta) data, but can also be configured with appropriate […]
Read moreSpotlight May 2021: Towards safe and sustainable innovation in nanotechnology: State-of-play for smart nanomaterials
The European Commission’s new Action Plan for a Circular Economy Green Deal, the new European Industrial Strategy as well as the Chemicals Strategy for Sustainability presented in October 2020 are ambitious plans to achieve a sustainable, fair and inclusive economy in the European Union. These strategies require that any new material or product must not […]
Read more