>
Spotlight July: Plastic Pollution and the Urgent Need for Comprehensive Action
>
Spotlight July: Plastic Pollution and the Urgent Need for Comprehensive Action
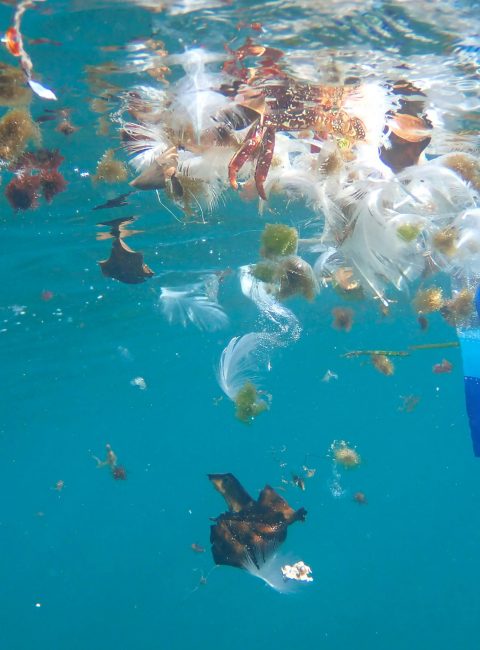
Plastic pollution has become a significant threat to the oceans, biodiversity, and ecosystems worldwide. Despite efforts to reduce plastic consumption, escalating plastic production continues to increase the magnitude of plastic pollution in the environment. In response to this crisis, the UN-Environmental Assembly (Link) adopted a resolution in March 2022 to develop a legally binding treaty to address global plastic pollution. However, the resolution falls short in addressing toxicity risks associated with plastics.
The article by Alva et al. proposes categorizing plastics as Persistent, Bioaccumulative, and Toxic (PBT) pollutants, considering their long-range transport and harmful effects on the environment. By applying the PBT framework, governments can control or eliminate the manufacture and use of harmful plastics. The article provides scientific evidence supporting the PBT criteria, highlighting the persistence, bioaccumulation potential, and toxicity of plastics. The adverse effects caused by plastic particles are attributed to both physical characteristics and chemicals leaching from the plastic. Chemicals added during production, as well as pollutants sorbed from the environment, contribute to the toxicity.
The adoption of the PBT framework is crucial to mitigate micro- and nanoplastic pollution, reinforcing the UNEA-Treaty and promoting global plastic governance. Urgent policy decisions, along with regulatory enforcement, are needed to cap and reduce plastic production and implement sustainable end-of-life solutions. Equitable interventions and equal access to pollution prevention strategies are vital to address the inequality gap and promote environmental justice in plastic pollution management.
Original Publikation:
Alava, J J et al. (2023). A Call to Include Plastics in the Global Environment in the Class of Persistent, Bioaccumulative, and Toxic (PBT) Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 22, 8185–8188.

Weitere Spotlights
Spotlight February 2023: New sustainable and promising method to give cotton textiles an antiviral and antibacterial finish
Textiles have been the subject of research into functionalization for many years, especially also to repel bacteria and viruses. Since the development of nanotechnological processes, there have been many attempts to incorporate UV protection with nano-titanium dioxide, or to provide textiles with anti-bacterial properties with nanosilver (see cross-sectional text “Nanoparticles in Textiles”). But nanosilver has […]
Read moreSpotlight June 2023: New catalytic process for recovering important materials from composites in a single process
Previously virtually impossible and a huge problem: fibre-reinforced resin composites (epoxides) were not recyclable, and wind turbine rotor blades, for example, add up to a waste pile of 43 million tons by 2050. Researchers have now taken an important first step in “reprocessing” these composites and catalytically dissolving them so that the carbon fibres and […]
Read moreSpotlight June 2022: From small to clever – What does the future hold for the safety and sustainability of advanced materials?
The smallest particles in materials research, nanoparticles, have occupied us intensively for more than 20 years to elucidate and further investigate their safety for humans and the environment. Now, however, the development is going from “small = nano” to “clever = advanced”, as discussed in a contribution by international scientists. Thereby, it is a great […]
Read moreSpotlight March 2022: Safe Materials from Scratch – Safe-by-Design-Concept in action
In recent decades, German research on nanomaterials and new, innovative materials has been widely expanded by material safety aspects. European initiatives also pay significant attention to this: both the European Union (EU) Green Deal, and the Chemicals Strategy for Sustainability (CSS) aim to create a sustainable, climate-neutral economy with sustainable and safe chemicals and products, […]
Read more