>
Spotlight June 2022: From small to clever – What does the future hold for the safety and sustainability of advanced materials?
>
Spotlight June 2022: From small to clever – What does the future hold for the safety and sustainability of advanced materials?
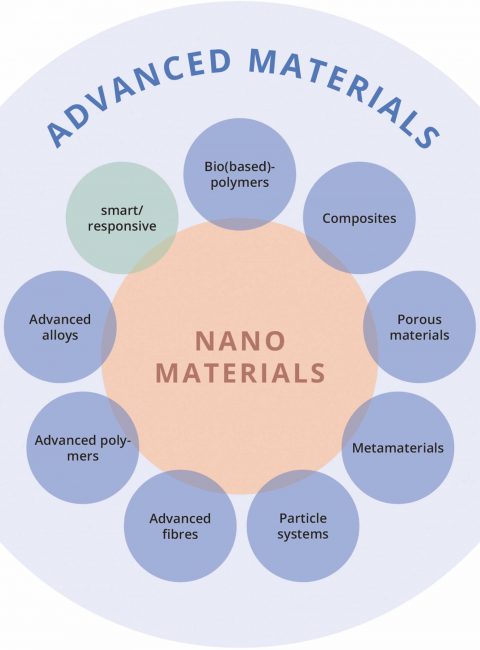
The smallest particles in materials research, nanoparticles, have occupied us intensively for more than 20 years to elucidate and further investigate their safety for humans and the environment. Now, however, the development is going from “small = nano” to “clever = advanced”, as discussed in a contribution by international scientists. Thereby, it is a great advantage to learn directly from the developments and achievements in the safety research of nanomaterials or to be able to transfer and apply them to advanced materials as well. In addition to the question “What is actually advanced or smart”, the demand for “Safe and sustainable by design (SSbD)” is also raised and the associated challenges are addressed. Important criteria for research here are the possibilities of characterizing the object of investigation, i.e. the concrete description of an advanced material, as well as the quality of the data generated and the data management. Again, the need for close collaboration between scientists from different disciplines with other stakeholders such as industry or regulatory authorities is pointed out. The authors make the important observation that nanosafety research to date has provided and will further provide the tools to meet this new challenge as well.
In doing so, they draw attention to three important prerequisites:
- The extension from “nano” to “advanced materials” should be based on technical criteria and include modelling as well as grouping approaches.
- Furthermore, sustainability should be integrated into the new material designs.
- And finally, these two principles should be firmly anchored in research, innovation and regulation to ensure a smooth transition to the implementation of the new and innovative materials.
Original publication:
Valsami-Jones, E et al. (2022). From small to clever: What does the future hold for the safety and sustainability of advanced materials? Nano Today, 42
Weitere Spotlights
Spotlight December 2022: Fighting tumors with micro robots
When we, the DaNa team as operators of the website nanopartikel.info, write about nanobots, i.e. nanometre-sized machines, we point out that these machines belong to science fiction, may even remain a utopia – i.e. never realisable. On the significantly larger micro-scale, however, small machines are conceivable that could help in the therapy of diseases, e.g. […]
Read moreSpotlight August 2020: The nanoGRAVUR Grouping approach
In August, we would like to present a paper of the German BMBF project nanoGRAVUR. nanoGRAVUR dealt from 2015-2018 with the grouping of nanostructured materials with regard to occupational safety, consumer and environmental protection and risk mitigation. The approach is now described by the project partners in this paper.Due to the variety of synthetic nanomaterials and the numerous modifications (differences in size, shape, chemical composition and surface functionalization), the effort required to investigate effects and behaviour within the framework of regulatory requirements is…
Read moreSpotlight November 2022: Photonics in nature and bioinspired designs
Science has always taken nature as a model and imitated it. If you look at the field of photonics, i.e. the use of optical technologies for information processing, transmission or storage, the colorful examples in the animal and plant world are perfect basic drawers for technical applications. While colors in nature are used either for […]
Read moreSpotlight December 2020: Rethinking Nanosafety – Part II
In December we would like to draw attention to the special issue: Rethinking Nanosafety – Part II in small. In the July Spotlight we already presented Part I. This special issue “Rethinking Nanosafety – Part II” also features research papers by renowned scientists in the field of nanosafety research. The first part of this special […]
Read more